What is TMR surgery?
AOFE Clinics specializes in TMR, a groundbreaking procedure that has transformed the lives of amputees by enhancing their ability to regain functional control over prosthetics. This innovative surgical approach involves the rerouting of nerves from amputated limbs to intact muscles nearby. As the healing process unfolds, AOFE’s skilled team of experience experts and surgeons work closely with patients to fine-tune every step of the TMR process. This partnership ensures not only effective healing but also an improved quality of life for amputees as they seamlessly integrate their prosthetics into daily activities.
Unlike bone, muscle, blood vessels and skin, the nerve remains alive and well after amputation. After transection, the nerves will bud and grow into the surrounding scar tissue and form a neuroma. This is one of the peripheral nervous system mechanisms that can contribute to neuropathic and phantom pain. Pain can be induced by spontaneous ectopic activity in these nerve endings or by chemical and mechanical stimulation. Although all transected nerves form neuromas, not all neuromas cause neuropathic or phantom pain.
The length of your hospital stay may vary depending on the complexity of the surgery, and some patients may require a longer recovery period. It is important to learn about your treatment options, as well as your rights as a patient, before making a decision.
At AOFE Clinics, we provide detailed content and resources to guide you through the process. You can search for additional information using the links below, where you will also find important resources regarding your care and our services.
Who is eligible for TMR (Targeted Muscle Innervation)?
- Neuropathic complaints in the socket or with bone-anchored prosthesis
- There is a clear causal relationship between the complaints and the findings during clinical examination and/or imaging research
Potential benefits of TMR may include:
- Reduction in the occurrence and severity of stump pain and phantom limb pain
- Possibility of improving control of prosthetic arm/leg/hand when combined with bone-anchored prosthesis
Potential disadvantages of TMR may include:
- Wound problems, infection or local bleeding
- Residual complaints or increase in stump and/or phantom pain
Who is not eligible for TMR (Targeted Muscle Reinnervation)?
- The complaints in the socket or with bone-anchored prosthesis are not neurophatic in nature
- If no causal relationship can be demonstrated between the complaints and the findings on clinical and/or imaging examination
Who is not eligible for TMR (Targeted Muscle Reinnervation)?
- The complaints in the socket or with bone-anchored prosthesis are not neuropathic in nature
- If no causal relationship can be demonstrated between the complaints and the findings on clinical and/or imaging examination
Targeted Muscle Reinnervation when you have painful swellings or limb pain
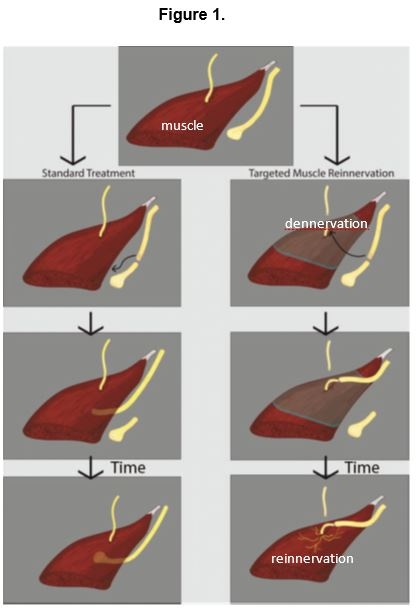
For painful swelling at the end of nerves in an amputation stump or for nerve pain that cannot be treated with analgesics, a so-called “targeted muscle reinnervation” or “targeted nerve/muscle restoration” operation can be performed. This operation involves precise suturing of nerves that controlled the forearm or lower leg muscles but have become idle due to the amputation of the motor nerve unit of the remaining muscles of the stump. That way, the idle nerve is given something to do again, giving the signals fired in the brain a purpose. After decades of research on how to treat neuromas, this is a promising development for people with amputation and nerve pain.
Who can benefit from Targeted Muscle Reinnervation surgery?
Those interested in the procedure to better control their prosthetic arm must undergo a medical review to determine their eligibility. In general, patients must meet the following criteria:
- Amputation above the elbow or at shoulder within previous ten years as stated in the medical records
- In case of stable soft tissues
- Willing to participate in rehabilitation
Comprehensive Care and Support
At AOFE Clinics, we understand the challenges and struggles faced by patients who experience painful swellings or limb pain after amputation. We are proud to offer advanced and innovative treatments, including Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR), to alleviate discomfort and enhance the quality of life for individuals in need. Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR) is a groundbreaking surgical technique that aims to relieve painful swellings and phantom limb pain. It involves the rerouting of nerves from the residual limb to selected target muscles. By providing the nerves with a new pathway, TMR helps reduce pain signals and offers patients an opportunity to regain control over their bodies. During the TMR procedure, our skilled and experienced surgeon identify nerves in the residual limb that were previously connected to the amputated limb. These nerves are then surgically redirected to nearby muscles that have lost their function due to the amputation. By connecting the nerves to these target muscles, TMR allows patients to control the movement of the artificial limb intuitively.
AOFE Clinics, often situated within university-affiliated hospitals, offers cutting-edge care that caters to the unique needs of patients. The clinics boast streamlined appointment scheduling, extended operating hours, and multiple locations, making it convenient for TMR recipients to access the specialized care they require. By choosing AOFE Clinics, patients can skip the traditional challenges associated with prosthetic fittings, experiencing a higher level of care and attention. In addition to its transformative impact on patients, TMR surgery opens up new avenues for medical professionals who are dedicated to making a lasting difference in the lives of others. AOFE Clinics not only sets a new standard in limb loss rehabilitation but also provides exciting career opportunities for doctors and surgeons looking to specialize in this cutting-edge field.
Benefits of TMR:
- Pain Reduction: TMR has shown remarkable success in alleviating phantom limb pain and reducing painful swellings. By rerouting nerves, the sensation of pain is diminished, offering relief and improving overall well-being.
- Enhanced Prosthetic Control: With TMR, patients experience improved control and functionality of their prosthetic devices. By connecting nerves to specific target muscles, the individual can achieve more natural and intuitive movement, leading to increased independence and a higher quality of life.
- Psychological Well-being: Chronic pain and discomfort can have a profound impact on a person’s mental health. TMR not only addresses physical pain but also contributes to psychological well-being by restoring confidence and reducing anxiety associated with pain.
- Long-Term Solutions: TMR provides long-lasting results, making it an effective treatment option for patients seeking a sustainable solution for their post-amputation pain management.
Please contact us for more information or signup online using or register form.
For copyright information and your patient rights, please refer to the resources on this page.
