What is osseointegration?
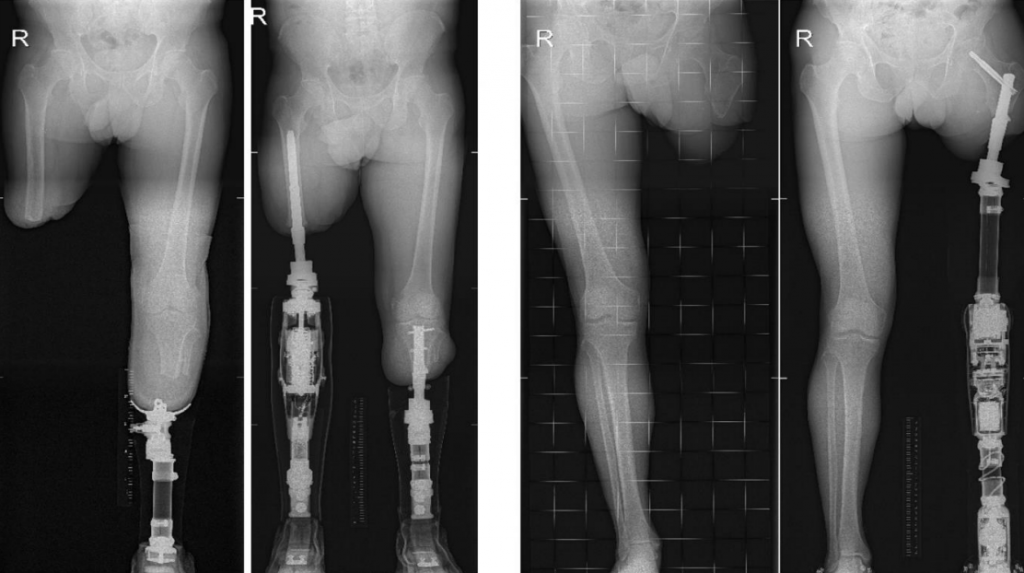
For patients with amputation of an arm or leg who experience problems wearing a socket prosthesis, the prosthesis can also be anchored directly to the body. The surgeon places an orthopaedic implant directly into the bone of the stump. The prosthesis can be connected to this implant using a click system. This technique is called osseointegration, and the prosthesis is therefore called click prosthesis. Doctors use the term osseointegration prosthesis or bone-anchoring prosthesis. The skin opening through which the implant protrudes is called a stoma.
What is the principle of osseointegration?
Bone anchoring comes from dentistry. In the 1960s, it was discovered by Swedish scientist Brånemark that bone adheres very well to the surface of a titanium screw. This connection of metal to bone is called osseointegration, and this principle is now used by orthopaedists to fit hip and knee replacements to the bone on a large scale. Since the 1990s, this osseointegration technique has been further developed for people with finger, arm or leg amputations. Unlike a hip or knee prosthesis, here the implant protrudes through the skin so that an artificial arm or leg can be clipped onto it. Since 2009, the osseointegration (click) prosthesis has also been used in the Netherlands and is currently experiencing spectacular growth.
Is an osseointegration (click) prosthesis safe?
Yes, this is a safe treatment. Surgeon Dr Jan Paul Frölke and rehabilitation specialist Dr Henk van de Meent and their research team at Radboudumc Nijmegen, in collaboration with other major centres around the world, have followed all patients they have treated with osseointegration prosthesis since 2009. Not only have they investigated the benefits of this treatment, but they have also identified the disadvantages and possible complications. Initially, it was thought that the implant would give rise to infection of the bone and loosening of the implant. Research published in US international scientific journals showed in the first 84 patients with an osseointegration prosthesis that the risk of loosening is very small. In 1 patient, the implant loosened and had to be replaced. Follow-up studies could confirm this, but more than two-thirds of people were found to have regular ostomy irritation and ostomy infections. Particularly in people who smoked and those with high body weight. However, the ostomy symptoms were easily treatable and often transient. Due to recently developed new surgical techniques, ostomy problems are now rare and the symptoms are fewer. Ostomy complaints are now seen mostly in the first two years after surgery.
What are the advantages of an osseointegrated (click) prosthesis?
The advantages of the osseointegration (click) prosthesis over the socket prosthesis were found to be significant after only one year, but this improvement also continues after two and five years. From studies in the first patients treated in the Netherlands, prosthesis wearing time increased significantly, walking distance increased and walking also took less energy. Quality of life increased and X-ray examination of the bone showed that the bone of the stump became stronger and thicker. A major advantage of the osseointegration prosthesis is that it is stably anchored to the bone. As a result, people feel more secure, can sit and cycle better, and in summer they do not suffer from perspiration. Another interesting advantage is that people with an osseointegrated prosthesis can feel the ground. The vibrations that occur when walking over a smooth or non-slippery surface are sensed through the implant in the bone. This phenomenon is called osseoperception (feeling with the bone) and gives the person with an osseointegration prosthesis the feeling of having his or her own leg back.
